
In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department. Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. As is the case when analyzing other variances, the direct material price variance needs to be assessed in the context of other relevant variances and factors, such as direct material price variance and direct labor variances. The management therefore needs to assess performance while taking all these relevant factors into account. The direct materials quantity variance of Blue Sky Company, as calculated above, is favorable because the actual quantity of materials used is less than the standard quantity allowed.
Formulas to Calculate Material Cost Variance and Material Price Variance
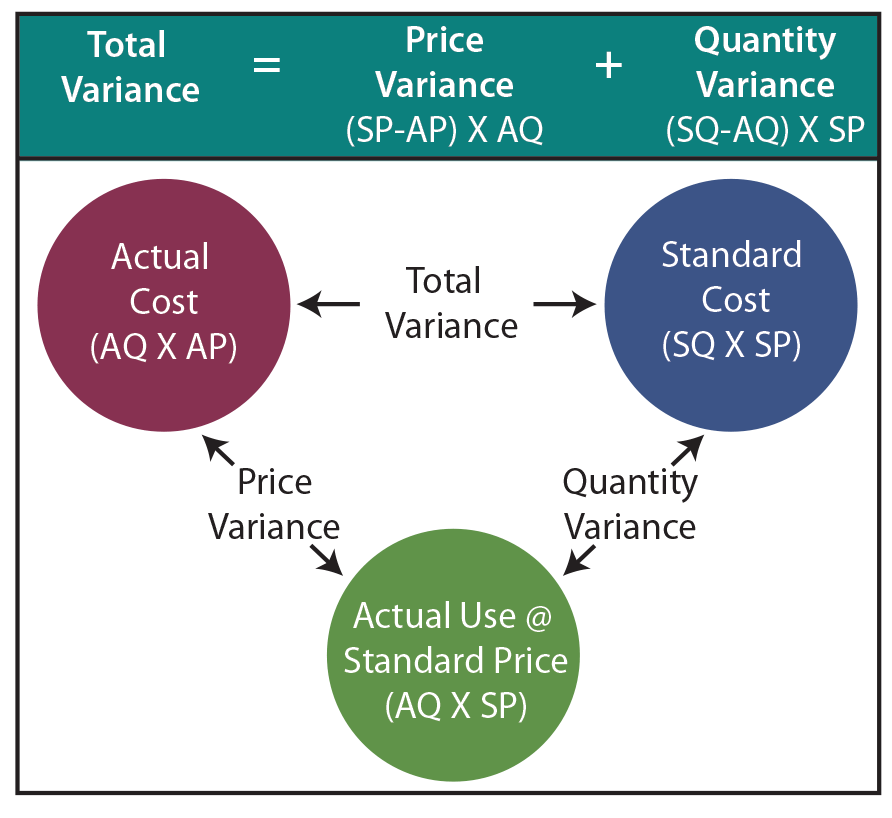
The actual cost less the actual quantity at standard price equals the direct materials price variance. The difference between the actual quantity at standard price and the standard cost is the direct materials quantity variance. Remember that a standard cost is the amount that you expect to pay for a good or service, especially when it comes to creating something.
What is direct material price variance?
- The material quantity variance in this example is favorable because the company manufactured the output using a lesser quantity of materials than what was planned in the budget.
- Direct materials cost is the sum of all direct materials costs incurred during the accounting period.
- Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500). This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35. In this question, Angro has experienced an unfavorable direct materials quantity variance because the actual usage of materials (i.e., 8,000kgs) is more than the standard quantity allowed (i.e., 7,500 kgs) to manufacture 5,000 units pf product. In other words, when actual quantity of materials used deviates from the standard quantity of materials allowed to manufacture a certain number of units, materials quantity variance occurs. The direct materials quantity variance is one of the main standard costing variances, and results from the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity of material used by a business during production.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
In food service, the price of ingredients, such as milk and eggs, is always changing. When your business purchases others goods to produce your products, you must incorporate the cost of the supplies how to calculate dividend yield with a formula into your budgets at the beginning of the year and each month. Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners.
Purchase price variance
It can even be caused by the purchasing department ordering materials that have an excessively low quality, so that more material is scrapped during the production process. Standard direct material usage refers to the amount of materials allowed to be used per unit produced. If however, it is considered to be significant in relation to the size of the business, then the variance needs to be analyzed between the inventory accounts (raw material, work in process, and finished goods) and the cost of goods sold account. The first step in activity-based variance analysis is to assign all overhead costs to a level of activity. To reach this standard rate, the annual overhead cost is divided by the cost center’s practical capacity. Practical capacity is used so that idle capacity may be found and put to better use.
Direct Materials Quantity Variance Calculator Online
This calculation helps businesses understand the efficiency of their material usage and identify areas for improvement. The direct materials price variance of Hampton Appliance Company is unfavorable for the month of January. This is because the actual price paid to buy 5,000 units of direct material exceeds the standard price. Direct material quantity variance is calculated to determine the efficiency of the production department in converting raw material to finished goods. A negative value of direct material quantity variance is generally unfavorable and it implies that more quantity of direct material has been used in the production process than actually needed. A positive value of direct material quantity variance is favorable implying that raw material was efficiently converted to finished goods.
Whether it’s to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; people who rely on dummies, rely on it to learn the critical skills and relevant information necessary for success. Daniel S. Welytok, JD, LLM, is a partner in the business practice group of Whyte Hirschboeck Dudek S.C., where he concentrates in the areas of taxation and business law. Dan advises clients on strategic planning, federal and state tax issues, transactional matters, and employee benefits. He represents clients before the IRS and state taxing authorities concerning audits, tax controversies, and offers in compromise. He has served in various leadership roles in the American Bar Association and as Great Lakes Area liaison with the IRS.
Variances occur in most of the manufacturing processes and for almost all cost elements. The ultimate motive behind their calculation is to control costs and enhance improvement. The direct material quantity variance will be adverse if the actual quantity of fabric used in manufacturing 10,000 units of shirts is 30,000 meters and the standard amount of fabric allowed for a single shirt is 2.8 meters. A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials. An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, indicates that the amount of materials used exceeds the standard requirement.
An adverse or unfavorable material quantity variance occurs when the actual volume of materials used in production exceeds the standard quantity that is expected for the level of output in a period. This involves looking beyond the numbers to understand the underlying factors contributing to the variances. For example, if a material price variance is detected, managers should examine market conditions, supplier performance, and procurement strategies to pinpoint the cause. Similarly, if a material quantity variance is found, a thorough review of the production process, employee performance, and equipment efficiency is necessary. This investigative approach ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective. Direct materials actually cost $297,000, even though the standard cost of the direct materials is only $289,800.
Hence, the total material cost variance may result from the difference between the standard and actual quantities of materials used, the difference between the standard and actual prices paid for materials, or from a combination of the two. The following equations summarize the calculations for direct materials cost variance. For purposes of inventory calculation, the direct materials account includes the cost of materials used rather than materials purchased.



